Precision and grasping tools are important for successful surgical outcomes in the ever-evolving healthcare field. Among different general surgery instruments, Cheatle forceps excel as an essential grasping tool for surgical setups and sterilization processes. It is used to remove sterilized instruments from boilers and formalin cabinets. To understand the structure, operations, and features of this instrument, one needs to understand the Cheatle Forceps Diagram, which directly simplifies the instrument for the user. These instruments are made for efficiency and advancement in medical procedures. However, understanding the anatomy of the Cheatle Forceps Diagram is necessary to enhance your expertise in surgical procedures. In this blog, we’ll explore the diagram, parts, features, uses, and limitations of Cheatle Forceps in modern medical practices. Let’s take a closer look!
What are Cheatle Forceps?
Cheatle Forceps are versatile grasping tools used in various surgical procedures to hold and transfer sterilized instruments without infecting other items. Surgeons prefer these forceps because of their easy-to-hold design and tissue manipulation nature. They are used during different operations, including cystoscopy surgery, urethral dilatation, and stone removal. Moreover, they are placed in a container of methylated spirits when they are not used, for safety purposes. Before using this instrument, they are usually dipped in an antiseptic solution like Detol or Carbolic lotion.
You can also elevate your surgical expertise with our extensive range of Forceps.
Cheatle Forceps Diagram Overview
The Cheatle Forceps are long, robust instruments with remarkable curved blades, especially used for tissue dissection and manipulation. Inside the blade, there is a large serration which helps to get while taking instrument vessels or linen. However, as it is long enough and good with serration, sterilize instruments can be safely transported from one tray to another. Having a detailed look at the instrument, we can identify four major parts of Cheatle Forceps that work together to perform successful operations. The parts include Jaws, Box Lock or Locking Mechanism, Hinge Joint, and Finger Bow Handles.
Cheatle forceps parts
Like any other forceps, the Cheatle Forcep has some major parts that work together to perform successful work in the operational field. The key parts of this instrument include:
Jaws
The jaws have a tip shape with straight or curved structures to enhance usability. However, it also provides superior control of the sterilized instruments without causing any injury. Its working ends are mostly serrated and smooth.
Locking Mechanism/Box Lock
It includes a spring or ratchet mechanism to ensure the precision of the forceps while holding objects securely. It assures that the forcep remains closed at that time.
Hinge Joint
This pivot point connects the handles and the jaws, which directly enables effortless operation and an easy sterilization process after use.
Handles
This long, ergonomic design allows easy and secure grip on the instruments. The handles help in manipulation during the sterilization process with no damage.
Detailed Cheatle Forceps Diagram
The Cheatle Forceps is a well-thought-out design that provides durability and precision to the medical procedure. Following is the detailed diagram of this instrument.
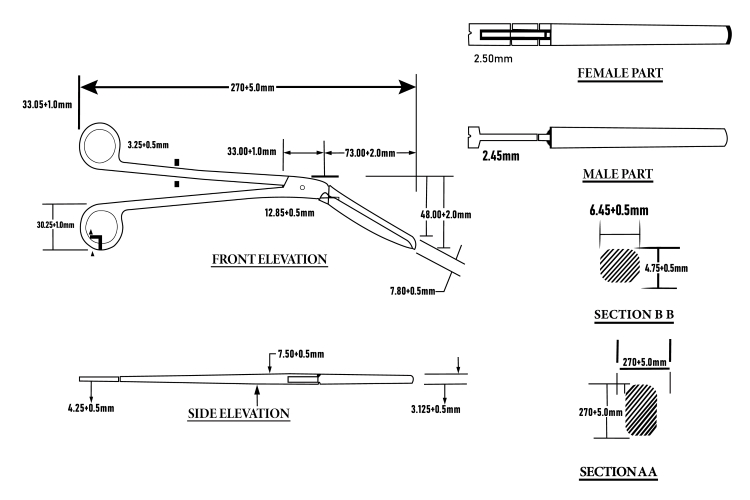
Front Elevation
The front elevation view features the most important key features that help in the functionality of the instrument, which are the jaws, hinge joints, and handles.
Parts | Description & Function | Measurements |
Jaws | The serrated tip of the jaw is connected to the box lock to grip the instruments securely. | 48.00 ± 2.0 mm & 7.80 ± 0.5 mm |
Handles | Rounded finger ring, visible to either side of the forceps to ensure a comfortable grip. | 33.05 ± 1.00 mm & 30.25 ± 1.00 mm |
Hinge Joint | Present in the middle of the jaws and handles to allow smooth movement. | 12.85 ± 0.5 mm |
Side Elevation
The side elevation highlights the lateral perspective, showing the shaft, hinge joint, handles, and jaws.
Parts | Description & Function | Measurements |
Shaft | The straight part of the forceps extends from the handles to the jaws to provide support. | 7.50 ± 0.5 mm |
Handles | Slightly angled handles grant visibility to the instrument’s shape for a comfortable grip. | 4.25 ± 1.00 mm |
Jaws | Smooth, curved jaws meet at a central point with the locking mechanism. | 3.125 ± 0.5 mm |
Hinge Joint | Precisely visible to this side to see proper open and close rotation. | |
Male and Female Parts
This tool has two main intersecting parts that fit together, the male and female parts.
Parts | Description & Function | Measurements |
Male Part | The jaw section with a serrated tip that fits into the female part performs its functions. | 2.45 mm |
Female Part | It is the handle and receiving mechanism, aligning with the male part to secure and handle objects. | 2.50 mm |
If you want a similarly structured forcep, Learn about Kocher Artery Forceps.
Uses
Cheatle Forceps are versatile forceps that offer different benefits. Some of the uses include:
- Used to hold and manipulate tissues during surgeries.
- Helps in tissue dissection and manipulation.
- Transfer sterilized instruments to surgical tables.
- Aids in post-sterilization by arranging and handling different surgical instruments.
- Prevent slippage of instruments by providing a tight grip.
- Grants control and prevents user fatigue due to finger handles.
- Reduce damage or infection chances to other items.
Explore Kelly’s long forceps for having another similar instrument.
Prominent Features and Benefits
There are several features and benefits of the Cheatle forceps that help in understanding it for better use, which include:
Features | Benefits |
Stainless Steel Construction | Manufactured from high-quality stainless steel. |
Curved, Locking Design | Grant superior control of tissue with no slipping chances. |
Blunt, Flat Tips | Handle delicate structures with reduced damage risk. |
Ergonomic Handle Design | Provide control and holding comfort. |
Variety | Available in different sizes to accommodate surgeries. |
Lightweight | Reduce hand fatigue during long procedures. |
Durable Construction | Corrosion resistance made it feasible for longer use. |
Sterility Maintenance | Sterilize the instruments without degrading them. |
Limitations
Every instrument has limitations, and understanding them for the users is crucial for successful surgical outcomes. The limitations of this Cheatle Forceps Diagram are as follows:
- It might damage delicate tissues with excessive force if not held carefully.
- The specific design results in limited reach.
- Improper sterilization will cause infection.
- If untrained, you have to face complexity in handling.
- Jaws and tips might get damaged due to not securing them safely.
Conclusion
Cheatle Forceps are important instruments for ensuring sterility during surgical procedures. Understanding the components and functions of these forceps improves their effectiveness in medical procedures. However, their major parts, including the handles, hinge, and jaws, are meticulously designed to ensure precise control and secure handling of sterilized instruments. Also, the features, uses, and limitations of this instrument should be completely understood by the users to enhance its usability and reduce potential complications.
At Surgetronix, we take pride in manufacturing high-quality Cheatle forceps. Our products are crafted with precision engineering and premium materials to meet the rigorous demands of healthcare professionals. Our reliable and durable surgical instruments uphold the highest standards of medical care.
About The Author

Hidayatul Haq
He is a seasoned SEO professional with three years of experience, currently leading the SEO team at Surgitronox. As a top-rated freelancer on Upwork and Fiverr, he has successfully completed numerous projects, consistently delivering exceptional results.

